Introduction to Forex Volatility Analysis
In the fast-paced world of Forex trading, one of the most critical factors that can significantly impact your trading success is volatility. Understanding and mastering Forex volatility analysis can make the difference between profitable trades and significant losses.
What is Forex Volatility Analysis?
Forex Volatility Analysis is a fundamental aspect of currency trading, essential for traders seeking to navigate the intricate dynamics of the foreign exchange market. It serves as a compass, allowing traders to gauge and harness the degree of price fluctuation or volatility that characterizes the market at any given time.
In essence, Forex Volatility Analysis revolves around meticulously scrutinizing the ebbs and flows in the prices of currency pairs over a predefined time frame. This meticulous examination serves a dual purpose – it not only unveils the inherent volatility within the Forex market but also empowers traders with the insights required to seize trading opportunities while managing the inherent risks.
Volatility, in the context of the Forex market, is akin to the heartbeat of the financial world, constantly pulsating and responding to a myriad of external stimuli. This pulsation is driven by a multitude of factors, each carrying its own weight in influencing market dynamics.
Factors Influencing Forex Market Volatility:
- Economic Data Releases: Economic indicators such as GDP figures, employment reports, and inflation data wield a significant influence on market sentiment. Positive or negative surprises in these releases can trigger sharp market movements.
- Geopolitical Events: International developments, such as political elections, trade negotiations, or geopolitical tensions, can inject a dose of uncertainty into the Forex market, spurring rapid price shifts.
- Central Bank Policies: Decisions and statements from central banks, particularly regarding interest rates and monetary policy, are closely monitored by Forex traders. Changes in policy direction can lead to volatile market reactions.
- Market Sentiment: Trader sentiment can be contagious. Positive sentiment can lead to bullish runs, while a pessimistic mood can trigger market sell-offs.
Understanding the ebb and flow of volatility is paramount for Forex traders, as it serves as a compass that guides them through the tumultuous seas of currency trading. When volatility is high, it signifies that the market is experiencing pronounced price swings, creating opportunities for traders to capitalize on these rapid fluctuations. However, it also implies elevated risk, as sharp reversals can lead to substantial losses if traders are not adequately prepared.
Conversely, during periods of low volatility, the Forex market may seem tranquil, with prices moving at a slower pace. While this may make it challenging to identify immediate trading opportunities, it doesn’t mean that profitable trades are unavailable. Traders need to adapt their strategies to suit the prevailing market conditions, potentially employing range-bound or consolidation-based strategies.
In essence, Forex Volatility Analysis is the cornerstone of effective trading, offering traders the foresight to calibrate their strategies, manage risk effectively, and seize opportunities as they arise. It’s a skill that, when mastered, can become a powerful tool in the arsenal of any Forex trader, empowering them to navigate the ever-changing tides of the currency markets with confidence and precision.
Measuring Volatility
The Average True Range (ATR)
In the intricate world of Forex trading, mastering the art of measuring volatility is pivotal for traders seeking to navigate the market’s unpredictable terrain. Among the arsenal of tools available, the Average True Range (ATR) stands out as a cornerstone of volatility assessment. This remarkable indicator provides traders with valuable insights into the potential price fluctuations within currency pairs, empowering them to set informed stop-loss levels and position sizes.
Calculating the ATR
To harness the power of the ATR effectively, it’s crucial to understand how it’s calculated. The ATR formula is as follows:
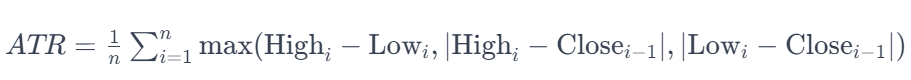
Breaking this formula down:
- (n) represents the number of periods considered for the calculation. Typically, traders use a 14-day period, but this can be adjusted to suit individual preferences.
- High and Low correspond to the highest and lowest prices recorded on day (i).
- {Close}{i-1}) represents the closing price on the previous day.
Interpreting ATR Values
The ATR indicator offers a numerical representation of market volatility. A higher ATR value indicates greater volatility, signifying that currency prices are prone to more extensive and rapid fluctuations. Conversely, a lower ATR value suggests relatively subdued volatility, where price movements are less dramatic and more predictable.
Practical Applications of ATR
Traders leverage the ATR in several ways:
- Optimal Position Sizing: ATR helps traders determine the appropriate size for their positions. In high-volatility environments, smaller positions may be preferred to mitigate risk, while larger positions can be considered in low-volatility conditions.
- Setting Stop-Loss Levels: The ATR can guide traders in establishing effective stop-loss levels. By factoring in the current market volatility, traders can position their stop-loss orders at levels that accommodate price fluctuations without triggering premature exits.
The Volatility Index (VIX)
Unveiling the Insights of the VIX
While the Volatility Index (VIX) is conventionally associated with the stock market, its applicability transcends asset classes, making it a valuable tool for Forex volatility analysis. Often referred to as the “fear gauge,” the VIX gauges market participants’ expectations of future volatility. When applied to the currency market, it provides essential insights into market sentiment.
Calculating the VIX
The VIX is derived from the implied volatility of options on the S&P 500 index. While the calculation is complex and beyond the scope of Forex trading, understanding its implications is crucial.
Interpreting VIX Readings
The VIX readings are clear indicators of market sentiment:
- High VIX: A high VIX value suggests that traders anticipate increased market volatility and heightened uncertainty. In the Forex market, this often translates to more significant price swings, providing traders with opportunities for potentially substantial profits.
- Low VIX: Conversely, a low VIX value indicates a more complacent market environment with lower expected volatility. During such periods, traders may encounter challenges in finding rapid, high-magnitude trading opportunities.
Utilizing the VIX in Forex Trading
While the VIX is not a direct indicator of Forex market volatility, it indirectly influences currency market sentiment. Forex traders can incorporate VIX readings into their broader analysis to gain insights into the broader financial market sentiment, which can, in turn, impact currency movements.
Incorporating both ATR and VIX into your Forex trading toolkit equips you with a multifaceted approach to measuring and adapting to market volatility. These tools empower you to make well-informed trading decisions, optimize position sizing, and set stop-loss levels that align with the ever-evolving dynamics of the currency market. By mastering the art of volatility assessment, you pave the way for enhanced trading success and risk management in the dynamic world of Forex trading.
Trading Strategies Based on Volatility
High Volatility Strategies
When the Forex market experiences high volatility, it becomes a fertile ground for traders seeking to capitalize on rapid price movements. However, it’s crucial to approach high volatility with a well-thought-out strategy. Here are some key aspects to consider when implementing high volatility strategies:
Identifying High Volatility with ATR and VIX
Before diving into high volatility trading, it’s essential to identify periods of elevated volatility accurately. ATR and VIX serve as reliable tools for this purpose. Keep a vigilant eye on these indicators to spot spikes in volatility resulting from events like economic data releases, geopolitical tensions, or unexpected news.
Using ATR for Entry and Exit
In high volatility conditions, preserving your capital and maximizing profit potential are paramount. ATR comes to your aid by helping you set wider stop-loss and take-profit levels. These wider levels align with the increased price fluctuations, reducing the risk of premature stop-outs. This strategic adjustment allows you to stay in the trade longer, increasing the opportunity for profit accumulation.
Examples of High Volatility Trading Setups
High volatility often translates to sharp and decisive price movements. Traders can harness these movements using various trading setups:
- Breakouts: During periods of high volatility, price often breaks through key support or resistance levels. Traders can identify these breakout points using technical analysis tools like trendlines, channels, and chart patterns. Breakout trading involves entering a position when price breaks above resistance or below support, anticipating a continued price movement in the breakout direction.
- Reversals: High volatility can also trigger sharp reversals in the market. Traders can look for signs of trend exhaustion, such as overextended price moves or divergence in technical indicators. When these reversal signals align with high volatility, traders can enter counter-trend positions, aiming to profit from the expected price correction.
By combining the insights from ATR and VIX with sound technical analysis, traders can develop a robust strategy for navigating high volatility markets.
Low Volatility Strategies
In contrast, low volatility environments require traders to adapt their strategies to the subdued market conditions. Here’s how traders can effectively trade during periods of reduced market movement:
Recognizing Low Volatility with ATR and VIX
Low volatility doesn’t mean trading opportunities are absent; rather, they require a different approach. ATR and VIX remain invaluable tools for identifying when market volatility is subdued. Low volatility can occur due to stable economic conditions or when the market enters a consolidation phase.
Patience and Range Trading
During low volatility periods, traders may shift their focus to range-bound strategies. Range trading involves identifying key support and resistance levels within which the price tends to oscillate. Traders buy near support levels and sell near resistance levels, aiming to profit from price movements within the established range. This approach requires patience, as traders wait for price to approach these levels before entering positions.
Volatility Breakout Strategies
Low volatility often precedes periods of increased market activity, characterized by volatility breakouts. Traders can prepare for potential breakouts by placing pending orders above and below the trading range. These orders are triggered when price breaks out of the range, allowing traders to participate in the ensuing price trend.
In conclusion, mastering both high and low volatility trading strategies is crucial for Forex traders. High volatility presents opportunities for rapid gains but demands careful risk management. Low volatility requires patience and adaptability to profit from range-bound conditions or prepare for upcoming breakouts. By integrating ATR and VIX analysis with effective trading techniques, traders can navigate the ever-changing Forex market with confidence and precision, regardless of the prevailing volatility.
Risk Management in Volatile Markets
In the world of Forex trading, effective risk management is not merely a choice; it’s an imperative, especially when navigating volatile markets. Volatility, characterized by sudden and unpredictable price movements, can be a double-edged sword, offering both opportunities and pitfalls. To safeguard your capital and trading success, consider the following risk management considerations:
Position Sizing
Position sizing is a fundamental aspect of risk management that directly relates to the level of volatility in the market. In highly volatile conditions, adjusting your position size is paramount. Here’s how it works:
- Reducing Position Size: During periods of extreme volatility, consider reducing your position size. Smaller positions limit potential losses. This cautious approach safeguards your capital when the market is in turmoil.
- Leveraging Volatility: Conversely, when volatility is relatively low, you may choose to increase your position size. Lower volatility implies reduced risk of rapid price fluctuations, allowing you to allocate more capital to your trades.
Position sizing is a critical element in managing risk because it ensures that each trade’s potential loss is proportionate to your overall risk tolerance and account size.
Stop-Loss Placement
Stop-loss orders are essential tools for limiting losses in volatile markets. However, the placement of stop-loss orders becomes especially crucial during periods of high volatility. This is where the Average True Range (ATR) comes into play:
- Using ATR for Stop-Loss Levels: ATR provides a valuable reference point for setting stop-loss levels that align with the current market volatility. During high volatility, ATR tends to be higher, indicating larger price swings. Therefore, setting tighter stop-loss levels can lead to premature exits. Conversely, during low volatility, ATR is lower, allowing for tighter stop-loss levels.
- Avoiding Tight Stop-Loss Orders: Placing tight stop-loss orders during periods of high volatility is risky, as they are more likely to be triggered by market noise and rapid price fluctuations. By referencing ATR and setting wider stop-loss levels, you give your trades more room to breathe and reduce the risk of getting stopped out prematurely.
Hedging Strategies
In times of extreme volatility, traditional risk management techniques may not always suffice. This is where hedging strategies come into play. Hedging involves taking offsetting positions to minimize potential losses. Here are some hedging techniques you can consider:
- Using Options: Options contracts provide a way to hedge against adverse price movements. For example, you can purchase put options to protect your long positions or call options to safeguard short positions. This strategy limits your potential losses while allowing you to participate in favorable price movements.
- Utilizing Correlated Currency Pairs: Another hedging technique involves trading correlated currency pairs. For instance, if you have a long position in one currency pair, you can open a short position in a correlated pair. This way, if one trade incurs losses due to volatility, the other can offset those losses, providing a degree of protection.
Hedging strategies should be used judiciously and in line with your overall trading plan. While they can mitigate risk, they also come with their own complexities and costs, so it’s essential to fully understand the mechanics before implementing them.
In conclusion, effective risk management is the bedrock of success in volatile Forex markets. Position sizing, stop-loss placement based on ATR, and hedging strategies are essential tools that help traders navigate the tumultuous seas of trading with confidence. By carefully calibrating your risk exposure and employing appropriate risk management techniques, you can weather the storms of market volatility and emerge as a more resilient and profitable Forex trader.
Case Studies
Case Study 1: High Volatility Scenario
Imagine you’re an experienced Forex trader, and you’ve diligently monitored the Average True Range (ATR) and the Volatility Index (VIX), which have both indicated a high volatility scenario looming on the horizon. You’re aware that economic data releases are about to impact the currency pair you’re trading.
Strategy for High Volatility:
- Widening Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels: Your first course of action is to adapt your risk management strategy to the heightened volatility. You decide to widen your stop-loss and take-profit levels based on the elevated ATR value. This strategic adjustment acknowledges that price fluctuations are likely to be more substantial during this period.
- News Monitoring: Given your keen interest in news and fundamental analysis, you closely monitor economic data releases and stay updated on any unexpected developments. In this high volatility scenario, you understand that even minor deviations from market expectations can trigger significant price movements.
- Executing the Trade: Armed with your analysis of the data release’s potential impact, you execute your trade with confidence. Your widened stop-loss levels provide a buffer to withstand the increased market noise and avoid premature exits, while the take-profit levels account for the extended price movements that often accompany high volatility.
This comprehensive approach to high volatility trading leverages the insights from ATR and VIX to optimize risk management and capitalize on potential profit opportunities amid market turbulence.
Case Study 2: Low Volatility Scenario
Now, let’s shift our focus to a different scenario – a period of low volatility where a currency pair is trading within a narrow range.
Strategy for Low Volatility:
- Tightening Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels: During periods of low volatility, you understand that price movements are relatively subdued. In response, you set tight stop-loss and take-profit levels, aligning them with the low ATR values. This approach is aimed at preserving capital and maximizing profit potential within the confined trading range.
- Patiently Awaiting Breakouts: Recognizing that price is consolidating within a narrow range, you exercise patience. Rather than actively trading within the range, you wait for a breakout opportunity. You place pending orders above and below the trading range, ready to participate when the market decides to make a decisive move.
- Adapting to Changing Conditions: Your flexibility shines during this low volatility scenario. As you wait for the market to show its hand, you continuously reassess your strategy and adapt to changing conditions. If you spot signs of an imminent breakout, you’re ready to adjust your positions accordingly.
This adaptive approach to low volatility trading allows you to conserve your trading resources while positioning yourself strategically for potential price breakouts. It reflects the importance of tailoring your strategy to the specific market conditions you encounter.
In conclusion, these case studies underscore the critical role of Forex volatility analysis in shaping effective trading strategies. By leveraging ATR and VIX indicators, traders can fine-tune their risk management, adjust their position sizing, and adapt their entry and exit levels to suit the prevailing volatility conditions. Whether the market is in a state of high turbulence or languishing in low volatility, a well-informed and adaptable approach can enhance your success as a Forex trader.
Tips for Effective Volatility Analysis
1. Regularly Monitor ATR and VIX:
Regular monitoring of the Average True Range (ATR) and the Volatility Index (VIX) is fundamental for any Forex trader aiming to excel in volatility analysis. Here’s how to leverage these indicators effectively:
- Consistency: Make it a routine to check ATR and VIX. Daily or weekly updates can help you stay well-informed about market volatility levels.
- Multiple Timeframes: Consider examining these indicators across various timeframes. Short-term fluctuations in volatility may differ from longer-term trends, and a comprehensive view can provide a more accurate picture.
2. Stay Informed:
Successful Forex traders are avid consumers of information. Staying informed about economic events, central bank decisions, and geopolitical developments is crucial, as these factors significantly impact currency markets:
- Economic Calendar: Use an economic calendar to keep track of scheduled economic releases, such as GDP reports, employment figures, and interest rate decisions. Be aware of their potential impact on currency pairs you are trading.
- News Sources: Follow reputable financial news sources to stay updated on the latest developments. Pay attention to breaking news that can trigger sudden market volatility.
- Central Bank Communication: Listen to central bank announcements and speeches, as these can offer insights into monetary policy changes that influence currency values.
3. Adapt to Market Conditions:
Market conditions are dynamic, and a one-size-fits-all approach to trading won’t suffice. Adaptability is key to effective Forex volatility analysis:
- Flexibility: Be flexible in your trading strategy. Recognize when market conditions are shifting from high to low volatility or vice versa. Adjust your position sizing, stop-loss levels, and trading style accordingly.
- Technical Analysis: Use technical analysis tools, such as trendlines, support and resistance levels, and chart patterns, to adapt to changing market conditions. These tools can help you identify breakout or reversal opportunities.
4. Practice Risk Management:
Risk management is the guardian of your trading capital, especially during volatile periods. Here’s how to prioritize risk management:
- Position Sizing: Align your position size with your risk tolerance and the prevailing volatility. Smaller positions during high volatility and larger ones in low volatility can help manage risk effectively.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Always use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. Base stop-loss levels on ATR to account for the current volatility. Avoid placing them too tightly during high volatility to prevent premature stop-outs.
5. Continuous Learning:
The Forex market is ever-evolving, and learning should be a constant pursuit for traders:
- Educational Resources: Invest in your trading education by reading books on Forex trading, taking online courses, and attending webinars. This ongoing learning will enhance your understanding of Forex volatility analysis.
- Trading Journals: Maintain a trading journal to record your strategies, decisions, and outcomes. Regularly reviewing your journal can help you identify areas for improvement.
- Community and Forums: Engage with the Forex trading community. Participate in forums and discussions to exchange ideas and gain insights from experienced traders.
In conclusion, effective Forex volatility analysis is a skill that can significantly enhance your trading success. By regularly monitoring ATR and VIX, staying informed about market events, adapting to changing conditions, practicing sound risk management, and continually learning and improving, you can navigate the dynamic world of currency trading with confidence and proficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering Forex volatility analysis is essential for traders looking to boost their trading success. By understanding and utilizing tools like ATR and VIX, traders can make more informed decisions, adapt to market conditions, and effectively manage risk. Whether you are trading during high or low volatility periods, incorporating volatility analysis into your strategy can help you navigate the dynamic world of Forex trading with confidence.
Remember that Forex trading involves risk, and there are no guarantees of profit. It’s crucial to develop a well-thought-out trading plan and practice disciplined risk management to achieve long-term success in this challenging but rewarding market.
Click here to read our latest article on The Role of Sovereign Wealth Funds in Forex
FAQs
- Why is monitoring ATR and VIX important for Forex volatility analysis? Monitoring ATR (Average True Range) and VIX (Volatility Index) is crucial because these indicators provide insights into the level of volatility in the Forex market. ATR quantifies price fluctuations, while VIX measures market participants’ expectations of future volatility. Regular monitoring helps traders make informed decisions and adjust their strategies based on the prevailing volatility conditions.
- How often should I check ATR and VIX? It’s advisable to check ATR and VIX regularly, ideally on a daily or weekly basis. This routine monitoring keeps you updated on changing volatility levels, enabling you to adapt your trading strategy as needed.
- What are some common sources of market-moving information I should stay informed about? Key sources of market-moving information include economic calendars for scheduled economic releases, reputable financial news sources for breaking news, and central bank announcements and speeches. These sources provide insights into events that can significantly impact currency markets.
- How do I adjust my trading strategy to changing market conditions? Adapting to market conditions involves flexibility. During high volatility, consider smaller position sizes and wider stop-loss levels. In low volatility, you can use tighter stop-loss and take-profit levels. Additionally, employ technical analysis tools like trendlines and support/resistance levels to identify suitable entry and exit points.
- What is the importance of risk management in volatile markets?Risk management is paramount during volatile periods because it safeguards your trading capital. Proper risk management involves adjusting position sizes based on volatility, setting appropriate stop-loss orders, and employing strategies to limit potential losses, ensuring you can weather market fluctuations.
- How can I determine the right position size during volatility analysis? Position sizing should align with your risk tolerance and the prevailing volatility. In high volatility, consider smaller positions to limit potential losses. In low volatility, you can allocate more capital to trades. ATR can guide you in determining appropriate position sizes.
- Why is it essential to use stop-loss orders, and how do I set them based on ATR? Stop-loss orders are essential to limit potential losses and protect your capital. To set them based on ATR, calculate a reasonable distance from your entry point using the ATR value as a reference. During high volatility, set wider stop-loss levels to account for larger price fluctuations.
- What role does continuous learning play in Forex volatility analysis? Continuous learning is vital because the Forex market is dynamic and ever-evolving. It helps traders stay updated on new strategies, tools, and market developments, enhancing their understanding of volatility analysis and improving their trading skills.
- What is the significance of maintaining a trading journal? A trading journal is a valuable tool for self-assessment. It allows you to record your trading strategies, decisions, and outcomes. Regularly reviewing your journal helps you identify strengths and weaknesses in your trading approach, facilitating continuous improvement.
- How can I engage with the Forex trading community and why is it beneficial? Engaging with the Forex trading community through forums and discussions allows you to exchange ideas, gain insights from experienced traders, and stay updated on industry trends. This interaction fosters a supportive network that can enhance your trading knowledge and skills.
Click here to learn more about Forex Volatility Analysis